Quick Start Guide
This guide will walk you through building a simple e-commerce domain model with DomainDrivenJS. By the end, you'll have a working model with value objects, entities, and aggregates that enforce business rules.
What We'll Build
We'll create a simplified e-commerce domain with:
- Products with price and inventory
- Orders with line items
- A basic order process flow
Setup
First, install DomainDrivenJS:
npm install domaindrivenjs zod
yarn add domaindrivenjs zod
pnpm add domaindrivenjs zod
Step 1: Create Value Objects
Let's start by creating a Money value object to handle monetary values:
import { z } from 'zod';
import { valueObject } from 'domaindrivenjs';
// Money value object representing an amount in a specific currency
export const Money = valueObject({
name: 'Money',
schema: z.object({
amount: z.number().nonnegative(),
currency: z.string().length(3)
}),
methodsFactory: (MoneyFactory) => ({
add(other) {
if (this.currency !== other.currency) {
throw new Error(`Cannot add ${other.currency} to ${this.currency}`);
}
return MoneyFactory.create({
amount: this.amount + other.amount,
currency: this.currency
});
},
multiply(factor) {
return MoneyFactory.create({
amount: this.amount * factor,
currency: this.currency
});
},
format(locale = 'en-US') {
return new Intl.NumberFormat(locale, {
style: 'currency',
currency: this.currency
}).format(this.amount);
}
})
});
// Let's test our Money value object
const price = Money.create({ amount: 10.99, currency: 'USD' });
const tax = Money.create({ amount: 0.55, currency: 'USD' });
const total = price.add(tax);
console.log(total.format()); // $11.54
Value objects are immutable and equality is based on their attributes rather than identity. If two Money objects have the same amount and currency, they're considered equal.
const price1 = Money.create({ amount: 10.99, currency: 'USD' });
const price2 = Money.create({ amount: 10.99, currency: 'USD' });
console.log(price1.equals(price2)); // true
Step 2: Create Entities
Now, let's create a Product entity that has an identity and can change over time:
import { z } from 'zod';
import { entity } from 'domaindrivenjs';
import { Money } from './money';
export const Product = entity({
name: 'Product',
schema: z.object({
id: z.string().uuid(),
name: z.string().min(1),
description: z.string().optional(),
price: Money.schema,
stockLevel: z.number().int().nonnegative(),
active: z.boolean().default(true)
}),
identity: 'id', // The property that uniquely identifies this entity
methodsFactory: (ProductFactory) => ({
// Decrease stock level (e.g., when ordered)
decreaseStock(quantity) {
if (quantity > this.stockLevel) {
throw new Error(`Insufficient stock: requested ${quantity}, available ${this.stockLevel}`);
}
return ProductFactory.update(this, {
stockLevel: this.stockLevel - quantity
});
},
// Increase stock level (e.g., when restocked)
increaseStock(quantity) {
return ProductFactory.update(this, {
stockLevel: this.stockLevel + quantity
});
},
// Update price
updatePrice(newPrice) {
return ProductFactory.update(this, { price: newPrice });
},
// Activate/deactivate product
setActive(isActive) {
return ProductFactory.update(this, { active: isActive });
}
})
});
// Let's use our Product entity
const keyboard = Product.create({
id: '123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000',
name: 'Mechanical Keyboard',
description: 'A premium mechanical keyboard with RGB lighting',
price: Money.create({ amount: 89.99, currency: 'USD' }),
stockLevel: 10
});
// Update the stock level
const updatedKeyboard = keyboard.decreaseStock(2);
console.log(keyboard.stockLevel); // 10 (original is immutable)
console.log(updatedKeyboard.stockLevel); // 8 (new instance with updated value)
Unlike value objects, entities have identity. Two products with the same attributes but different IDs are considered different entities.
Step 3: Create Aggregates
Aggregates are clusters of entities and value objects treated as a single unit. They enforce invariants (business rules) across the cluster.
Let's create an Order aggregate:
import { z } from 'zod';
import { aggregate } from 'domaindrivenjs';
import { Money } from './money';
export const Order = aggregate({
name: 'Order',
schema: z.object({
id: z.string().uuid(),
customerId: z.string().uuid(),
items: z.array(z.object({
productId: z.string().uuid(),
productName: z.string(),
quantity: z.number().int().positive(),
unitPrice: Money.schema
})),
status: z.enum(['DRAFT', 'PLACED', 'PAID', 'SHIPPED', 'COMPLETED', 'CANCELLED']),
placedAt: z.date().optional()
}),
identity: 'id',
invariants: [
{
name: 'Order must have items when placed',
check: order => order.status !== 'PLACED' || order.items.length > 0,
message: 'Cannot place an empty order'
},
{
name: 'Placed order must have placedAt date',
check: order => order.status !== 'PLACED' || order.placedAt !== undefined,
message: 'Placed order must have a placement date'
}
],
methodsFactory: (OrderFactory) => ({
// Add an item to the order
addItem(product, quantity) {
if (this.status !== 'DRAFT') {
throw new Error(`Cannot modify an order with status: ${this.status}`);
}
// Check if product exists in order
const existingItemIndex = this.items.findIndex(
item => item.productId === product.id
);
let newItems;
if (existingItemIndex >= 0) {
// Update existing item
const item = this.items[existingItemIndex];
const updatedItem = {
...item,
quantity: item.quantity + quantity
};
newItems = [
...this.items.slice(0, existingItemIndex),
updatedItem,
...this.items.slice(existingItemIndex + 1)
];
} else {
// Add new item
const newItem = {
productId: product.id,
productName: product.name,
quantity,
unitPrice: product.price
};
newItems = [...this.items, newItem];
}
return OrderFactory.update(this, { items: newItems });
},
// Place the order
placeOrder() {
if (this.status !== 'DRAFT') {
throw new Error(`Cannot place an order with status: ${this.status}`);
}
// The invariants will be checked automatically when we update
return OrderFactory.update(this, {
status: 'PLACED',
placedAt: new Date()
}).emitEvent('OrderPlaced', {
orderId: this.id,
customerId: this.customerId,
items: this.items,
placedAt: new Date()
});
},
// Cancel the order
cancelOrder() {
if (!['DRAFT', 'PLACED', 'PAID'].includes(this.status)) {
throw new Error(`Cannot cancel an order with status: ${this.status}`);
}
return OrderFactory.update(this, {
status: 'CANCELLED'
}).emitEvent('OrderCancelled', {
orderId: this.id,
cancellationReason: 'Customer requested cancellation'
});
},
// Calculate the total price of the order
getTotal() {
// Start with zero amount in the first item's currency (or USD if no items)
const currency = this.items.length > 0
? this.items[0].unitPrice.currency
: 'USD';
let total = Money.create({ amount: 0, currency });
// Add up all the line items
for (const item of this.items) {
const itemTotal = item.unitPrice.multiply(item.quantity);
total = total.add(itemTotal);
}
return total;
}
})
});
// Let's use our Order aggregate
const order = Order.create({
id: '123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174001',
customerId: '123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174002',
items: [],
status: 'DRAFT'
});
// Add an item
const orderWithItem = order.addItem(keyboard, 2);
// Calculate the total
const total = orderWithItem.getTotal();
console.log(total.format()); // $179.98
// Place the order - this will validate our invariants
const placedOrder = orderWithItem.placeOrder();
console.log(placedOrder.status); // PLACED
// This would throw an error due to invariant violation
try {
const emptyOrder = Order.create({
id: '123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174003',
customerId: '123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174002',
items: [],
status: 'DRAFT'
});
emptyOrder.placeOrder(); // Will throw - empty order cannot be placed
} catch (error) {
console.error(error.message); // "Cannot place an empty order"
}
Step 4: Handling Domain Events
Our placeOrder method emits a domain event. To listen for these events:
import { eventBus } from 'domaindrivenjs';
// Subscribe to the OrderPlaced event
eventBus.on('OrderPlaced', async (event) => {
console.log(`Order ${event.orderId} was placed at ${event.placedAt}`);
// Here you might:
// - Send a confirmation email
// - Reserve inventory
// - Update analytics
});
// When we place an order and save it, the event will be published
const placedOrder = order.addItem(keyboard, 2).placeOrder();
// In a real application, you would save this to a repository
// which would automatically publish the events
// orderRepository.save(placedOrder);
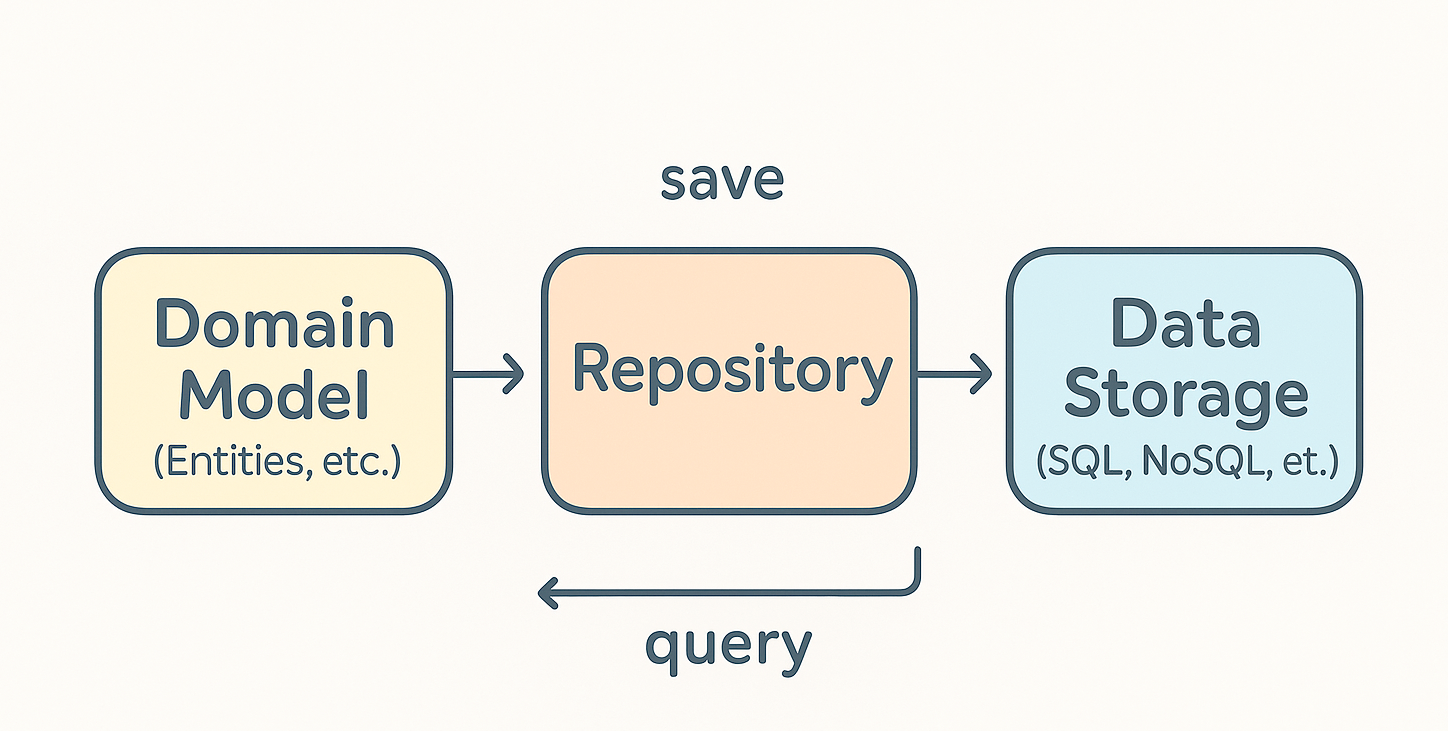
Step 5: Using Repositories
To persist our aggregates, we use repositories:
import { repository, createInMemoryAdapter } from 'domaindrivenjs';
// Create a repository for Orders
const OrderRepository = repository({
aggregate: Order,
adapter: createInMemoryAdapter({
identity: 'id'
})
});
// Save an order
await OrderRepository.save(placedOrder);
// Find an order by ID
const retrievedOrder = await OrderRepository.findById(placedOrder.id);
// Find orders by criteria
const draftOrders = await OrderRepository.findAll({ status: 'DRAFT' });
Complete Example
Here's how everything fits together in a complete example:
// Import dependencies
import { z } from 'zod';
import {
valueObject,
entity,
aggregate,
repository,
eventBus,
createInMemoryAdapter
} from 'domaindrivenjs';
// Define our domain model
const Money = valueObject({
name: 'Money',
schema: z.object({
amount: z.number().nonnegative(),
currency: z.string().length(3)
}),
methodsFactory: (factory) => ({
// Money methods...
})
});
const Product = entity({
name: 'Product',
schema: z.object({
id: z.string().uuid(),
name: z.string().min(1),
price: Money.schema,
stockLevel: z.number().int().nonnegative()
}),
identity: 'id',
methodsFactory: (factory) => ({
// Product methods...
})
});
const Order = aggregate({
name: 'Order',
schema: z.object({
id: z.string().uuid(),
customerId: z.string().uuid(),
items: z.array(z.object({
productId: z.string().uuid(),
productName: z.string(),
quantity: z.number().int().positive(),
unitPrice: Money.schema
})),
status: z.enum(['DRAFT', 'PLACED', 'PAID', 'SHIPPED', 'COMPLETED', 'CANCELLED']),
placedAt: z.date().optional()
}),
identity: 'id',
invariants: [
// Order invariants...
],
methodsFactory: (factory) => ({
// Order methods...
})
});
// Create repositories
const ProductRepository = repository({
aggregate: Product,
adapter: createInMemoryAdapter({ identity: 'id' })
});
const OrderRepository = repository({
aggregate: Order,
adapter: createInMemoryAdapter({ identity: 'id' })
});
// Set up event handlers
eventBus.on('OrderPlaced', async (event) => {
console.log(`Order ${event.orderId} was placed`);
// Process the order...
});
// Application logic
async function placeOrder(productId, customerId, quantity) {
// Get the product
const product = await ProductRepository.findById(productId);
if (!product) {
throw new Error('Product not found');
}
// Check stock
if (product.stockLevel < quantity) {
throw new Error(`Insufficient stock: requested ${quantity}, available ${product.stockLevel}`);
}
// Create order
let order = Order.create({
id: generateId(), // You would use a real UUID here
customerId,
items: [],
status: 'DRAFT'
});
// Add item to order
order = order.addItem(product, quantity);
// Place the order
order = order.placeOrder();
// Update product stock
const updatedProduct = product.decreaseStock(quantity);
// Save everything (in a real app, this would be in a transaction)
await ProductRepository.save(updatedProduct);
await OrderRepository.save(order);
return order;
}
// Helper function for demo - in real code, use a proper UUID library
function generateId() {
return '123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-' + Math.floor(Math.random() * 1000000000000).toString().padStart(12, '0');
}
// Usage example
async function run() {
// Create a product
const keyboard = Product.create({
id: generateId(),
name: 'Mechanical Keyboard',
price: Money.create({ amount: 89.99, currency: 'USD' }),
stockLevel: 10
});
await ProductRepository.save(keyboard);
// Place an order for the product
const order = await placeOrder(keyboard.id, generateId(), 2);
console.log(`Order placed: ${order.id}`);
console.log(`Total: ${order.getTotal().format()}`);
}
run().catch(console.error);
Next Steps
Now that you've built a basic domain model, you can explore:
Learn more about each core concept:
Check out complete examples:
Dive into advanced topics:
